- English
- Deutsch
Tag-driven ECM record automation
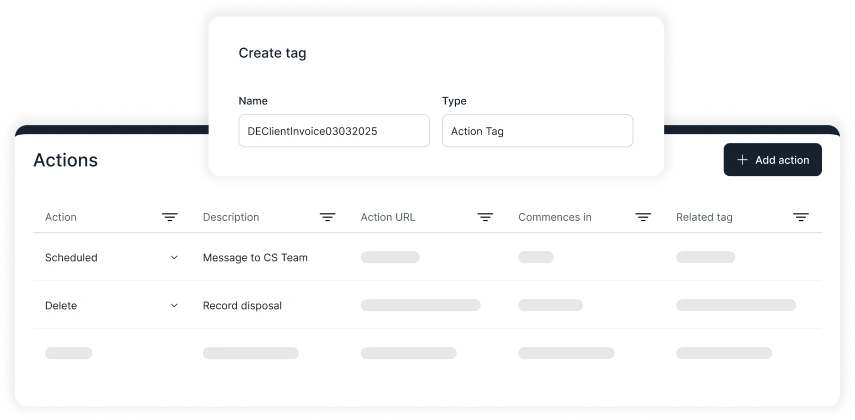
Data retention procedures are policies and practices that define how long organizations must store data and when it should be securely deleted. These procedures ensure compliance with legal, regulatory, and business requirements while minimizing security risks from storing unnecessary data.

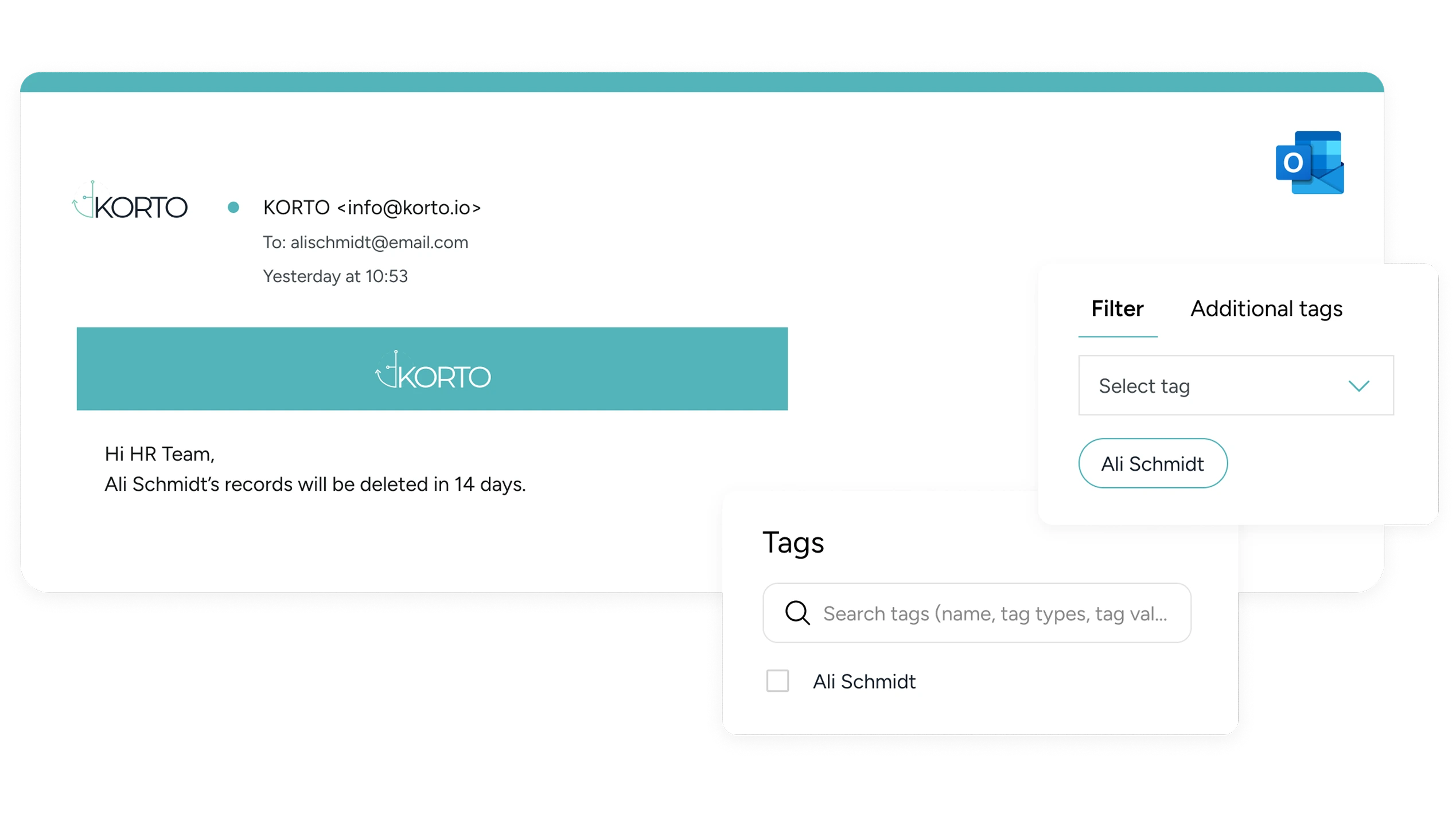
Launch the relevant workflows as you add a record to the KORTO system, and it will track retention and disposal timeframes.
Ensure compliance and boost efficiency with a secure solution that's simple to set up, use, and onboard.
Define workflows for all your teams and regions to ensure alignment with business, legal, and regulatory requirements.
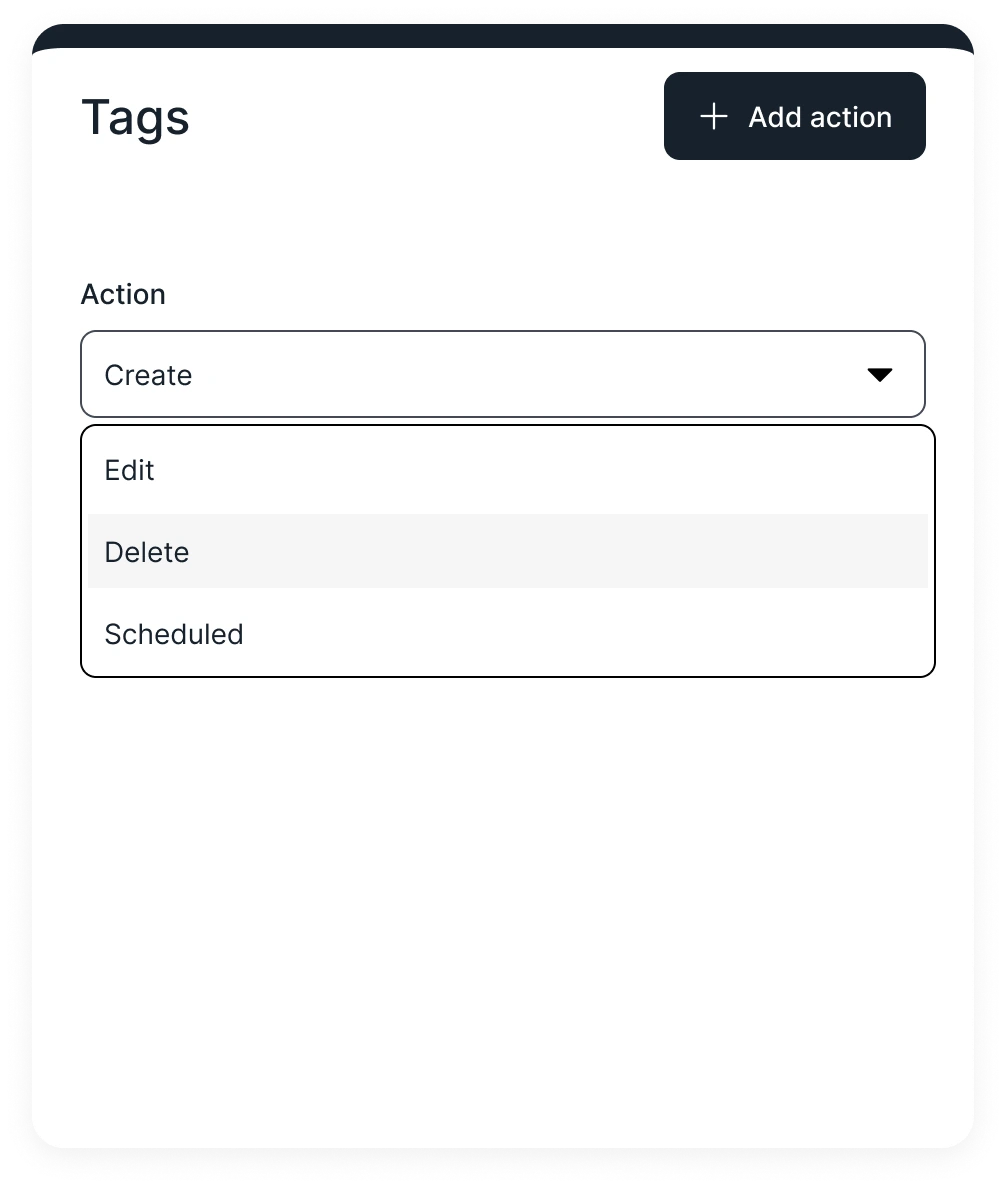

Flexible enough to meet every team's needs
Save time and find what you need quickly with KORTO's tag-based approach to Enterprise Content Management.
Read moreE-signatures and time stamps combine with KORTO's audit logs and blockchain integration for tamper-proof records.
Read moreKeep your records safe with KORTO’s secure cloud systems and APIs, granular access control, and blockchain technology.
Read moreDive into data retention periods in individual industries.
Read more about Data Retention Requirements by Industry